

This latency on counter updates and the use of a moving average may affect the throttling limit calculation and result in allowing requests over or denying requests under the current throttling limit.ĭepending on the distribution of your traffic on the network, the error margin over the last minute may range from a median of less than 10% for steady traffic rates up to about 20% of large sudden changes in traffic rates. To learn more about quota, see User quota.Ī throttling counter calculates the throttling limit by measuring the counter value every second and updating a moving average of 5 seconds.Įdge servers within the network share updated counter values with a delay ranging from 1 to 3 seconds. When you configure both quota and throttling for a given API key, API Gateway first applies throttling conditions, and based on whether the request was successful, increases the quota count for the API key. If a throttling counter reaches its limit, an API consumer will wait for a maximum of 5 seconds to regain the capability to make subsequent requests.
#Request throttled manual#
Once quota is full, it requires an automatic or manual reset to allow any subsequent requests with a given API key. The time period for API throttling always equals one second. You can schedule a quota window for the time periods of 1 hour, 6 hours, 12 hours, 1 day, 1 week, or 1 month. If you add another condition, for a key, throttling counter will be applied only to requests additionally including that key (logical operator: AND).
For example, if you configure throtling for an endpoint wiith two resources, counter will be applied for both (logical operator: OR). Note that depending on the conditions’ combinations, throttling counter may be applied to a specific resource. You can associate a throttling counter with the API key, HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, HEAD, PATCH, OPTIONS, DELETE), API resource and API endpoint conditions - key collections, API key, HTTP method, esource or endpoint.ĭepending on your configuration, a throttling counter may increase whenever an incoming request meets any of the above conditions, or a combination of these conditions. The quota limit increases whenever API consumers include API keys from that key collection in requests to your registered APIs. You can only associate quota with a key collection. If the average decreases below the specified requests-per-second limit, API consumers regain the capability to make requests that match the counter's associated conditions.Ĭached requests also count towards your throttling quota.

A throttling counter operates based on a moving average of received requests during the last 5 seconds.
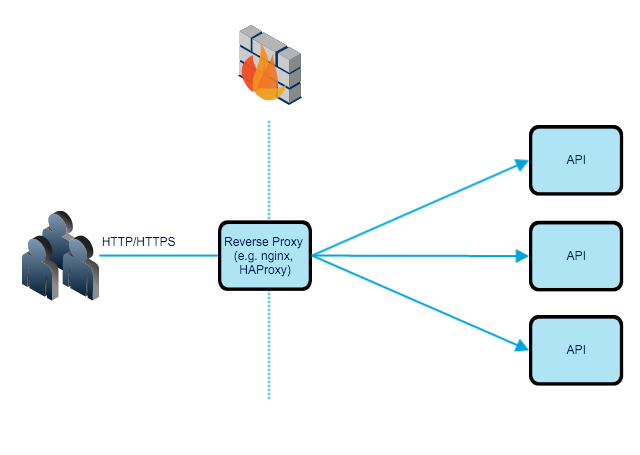
For each counter, you define a limit of allowed requests per second, and if that limit is reached, the edge server will reject any subsequent requests that match the counter's associated conditions. To throttle your API traffic, you create throttling counters that increment based on the incoming requests to your APIs.Ī throttling counter is an object composed of a set of conditions that, when matched by an incoming client request, cause the counter to increase. To learn more, see the Cloud Security documentation in the Protect section. To deal with this specific use case efficiently, Akamai recommends the Cloud Security products in tandem with API Gateway.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
